A car that won’t start can be incredibly frustrating. Often, the culprit is a faulty starter motor. Knowing how to repair a car engine starter can save you a significant amount of money and get you back on the road quickly. This guide will walk you through the process, offering practical advice and troubleshooting tips.
Learning how to repair a car engine starter isn’t as daunting as it sounds. With the right tools and a bit of patience, you can often diagnose and fix the problem yourself. This guide will delve into the common causes of starter failure, the steps to diagnose the issue, and how to replace or repair the starter. We’ll cover everything from testing the battery and starter solenoid to removing and reinstalling the starter motor. This will equip you with the knowledge to tackle this common car problem head-on. After this first paragraph, you might be interested in reading about how to repair your car’s garden how to repair gardery of alto car.
Understanding the Car Starter System
The starter system consists of a few key components working together: the battery, ignition switch, starter solenoid, and the starter motor itself. The battery provides the electrical power, the ignition switch activates the system, the solenoid acts as a relay, and the starter motor cranks the engine. Understanding how these components interact is crucial for effective diagnosis and repair.
Common Starter Problems
Several issues can prevent your starter from working correctly. These include a dead battery, a faulty solenoid, a bad starter motor, corroded connections, or damaged wiring. Pinpointing the exact problem is the first step in a successful repair.
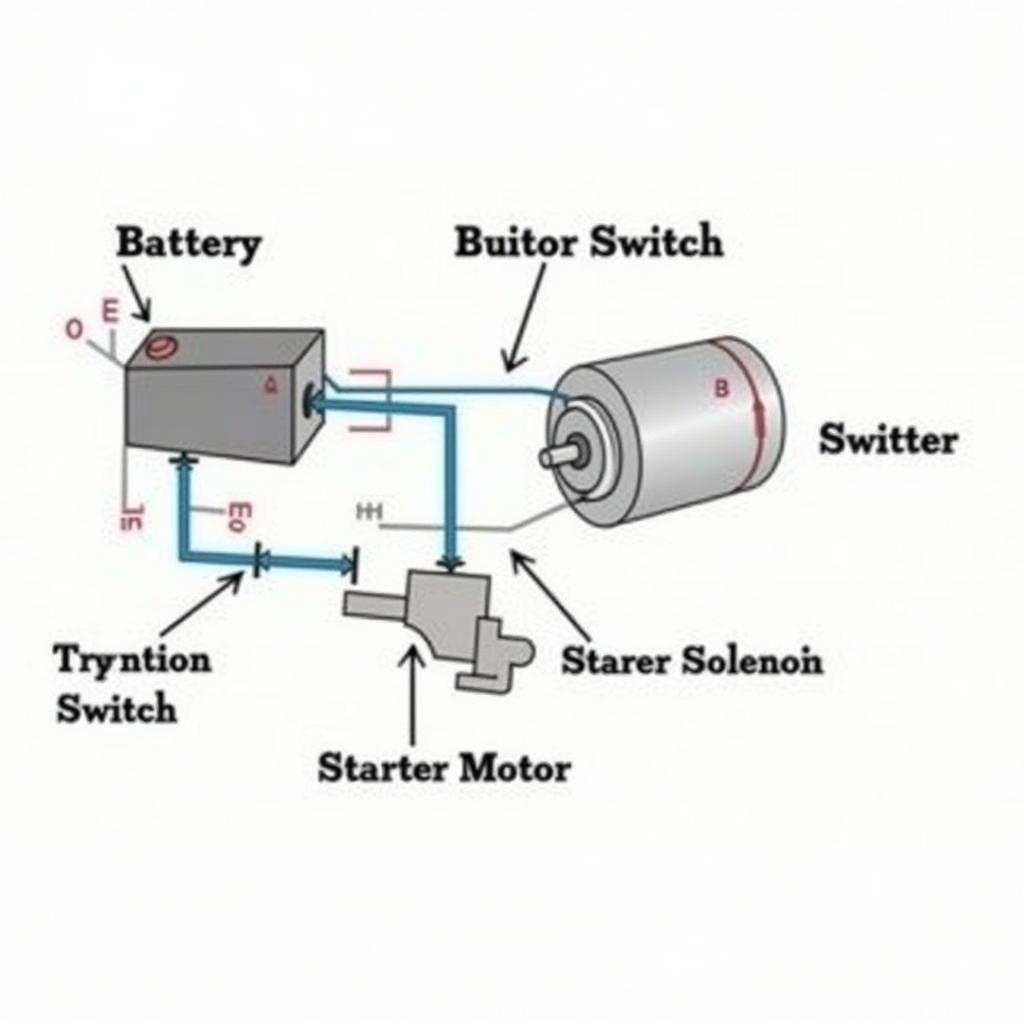 Car Starter Components Diagram
Car Starter Components Diagram
Diagnosing the Problem
Before you start taking things apart, it’s essential to diagnose the problem correctly. Begin by checking the battery. A weak or dead battery is the most common cause of starting problems. If the battery is okay, move on to checking the starter solenoid and motor. You can test these components using a multimeter or a test light.
Testing the Battery
Use a multimeter to check the battery voltage. A fully charged battery should read around 12.6 volts. If the voltage is significantly lower, the battery may need charging or replacement. You can also try jump-starting the car. If it starts with a jump, it points towards a battery issue.
Testing the Starter Solenoid and Motor
You can test the starter solenoid by using a multimeter to check for voltage at the solenoid’s terminals. If voltage is present but the starter doesn’t engage, the solenoid may be faulty. Similarly, you can test the starter motor by applying power directly to it. If the motor spins, the problem lies elsewhere in the system, perhaps with the ignition switch. Maybe you’re dealing with a more complex issue requiring a professional like those mentioned in what could be the car engine repair cost.
Repairing or Replacing the Starter
Once you’ve identified the faulty component, you can proceed with the repair or replacement. If the problem is with the solenoid or starter motor, you’ll likely need to replace the entire starter assembly.
Removing the Starter
Disconnecting the battery is the first step. Then, locate the starter, usually bolted to the engine block or transmission. Disconnect the electrical connections and remove the mounting bolts to free the starter.
Installing the New Starter
Install the new starter by reversing the removal process. Ensure all connections are secure and tight. Reconnect the battery and test the new starter. For less intensive repairs, check out how to car driver repair.
Preventing Future Starter Problems
Regular maintenance can help prevent future starter problems. Keep the battery terminals clean and free of corrosion. Ensure all connections are tight. Having your starter system inspected during regular car servicing can also help identify potential issues before they become major problems.
“Regularly cleaning battery terminals and ensuring tight connections can significantly extend the life of your starter motor,” says John Smith, Automotive Engineer at Smith Automotive Solutions. “These simple preventative measures can save you a lot of hassle and expense down the road.”
Conclusion
Knowing How To Repair Car Engine Starter problems can empower you to tackle this common issue effectively. By following the steps outlined in this guide, you can diagnose the problem, repair or replace the starter, and get your car back on the road. If your child’s toy car needs attention, you might find this helpful: how to repair kid remote car. Remember to prioritize safety and consult a professional if you are uncomfortable performing any of these steps. Regular maintenance is key to preventing future starter problems and ensuring the longevity of your vehicle’s starting system.
FAQ
- How much does it cost to replace a car starter? The cost can vary depending on the make and model of your car, but it typically ranges from $200 to $500.
- What are the symptoms of a bad starter? Common symptoms include clicking sounds when turning the key, grinding noises, the engine not cranking at all, or intermittent starting problems.
- Can I drive with a bad starter? No, once the starter fails completely, you will not be able to start your car.
- How long does a car starter last? A car starter typically lasts between 100,000 and 150,000 miles.
- How can I prevent starter problems? Regularly cleaning the battery terminals, ensuring tight connections, and having the starter system inspected during regular servicing can help prevent problems.
- Can I replace a car starter myself? Yes, with the right tools and some mechanical knowledge, you can replace a car starter yourself.
- What tools do I need to replace a car starter? You’ll need basic hand tools like sockets, wrenches, a ratchet, and possibly a jack and jack stands.
Common Starter Problem Scenarios:
- Clicking sound when turning the key: This often indicates a problem with the starter solenoid or a weak battery.
- Grinding noise when starting: This usually means the starter gear is not engaging properly with the engine flywheel.
- Engine cranks slowly: This could be caused by a weak battery, corroded connections, or a failing starter motor.
- Engine doesn’t crank at all: This could be due to a dead battery, a faulty ignition switch, a bad starter motor, or a blown fuse.
Related Articles and Further Reading:
For more information on car repairs, you can check out our articles on what repaires comes car is traveling.
Need Help? Contact Us!
If you need assistance with your car starter or any other automotive issue, please don’t hesitate to contact us. Our expert team is available 24/7 to answer your questions and provide support. You can reach us via WhatsApp: +1(641)206-8880, or Email: [email protected]. We’re here to help!